Theobromine is an alkaloid organic compound naturally found in cocoa beans. It’s similar to caffeine’s structure and functionality and is used as a flavoring agent in the food industry. It’s also used as a dietary supplement for its potential health benefits.
What is Theobromine?
Theobromine, or xantheose, is a bitter xanthine alkaloid with the molecular formula of C7H8N4O2. It is a dimethyl xanthine with two methyl groups at positions 3 and 7. Theobromine has one less methyl group than caffeine and can be a precursor for caffeine synthesis. Theobromine is a purine derivative and isomer of theophylline and paraxanthine.
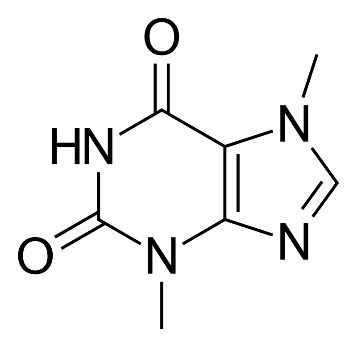
Theobromine chemical structure. Source: Wikipedia
How is Theobromine Produced?
Theobromine was first discovered as the principal alkaloid of cocoa beans in 1841 by Russian chemist A. Woskresensky. Cocoa bean husk also contains theobromine and is generally used as a substrate for extraction. Its concentration increases with fermentation. Apart from cocoa, theobromine is also found in coffee, tea, and kola nuts, as well as in several other lesser-known plants. The primary natural sources of theobromine are provided in the table below.
| Source | % Concentration |
| Cocoa Husk | 0.7-1.2 |
| Cocoa Beans | 1.5-3 |
| Green Coffee Beans | 20 mg/kg |
| Tea | 0.15-0.2 |
| Dried Mate | 0.3 |
In 1882, Hermann Emil Fischer reported that theobromine could be synthesized from xanthine. It can also be synthesized from 3-methyluric acid. However, chemical synthesis is not typical for commercial production.
Use of Theobromine in the Food & Nutrition Industries
Theobromine is used as an additive to flavor food products and is approved for use as a flavoring agent. It adds a chocolate-like bitterness to food products — and is increasingly used as a dietary supplement for potential health benefits.
Applications in the Food Industry
| Function | Applications |
| Flavoring Agent | Baked GoodsConfectionery and FrostingsGelatin and PuddingMilk ProductsSoft CandySweet Sauces |
Applications in the Nutrition Industry
Theobromine products may take various forms as a dietary supplement, including gels, suspensions, capsules or tablets, and powders. Because theobromine is nearly insoluble in water, aqueous formats are not used.
Theobromine has several potential health benefits, including the following:.
Mood Lifting
Certain studies suggest consuming theobromine from chocolate may have mild anti-depressive effects. One study reported that theobromine intake at normal levels (up to 250 mg) may positively affect mood.
Cardiovascular Function
Theobromine can act as a myocardial stimulant and vasodilator and can help regulate blood pressure and support healthy circulation by widening blood vessels. Certain studies also suggest its role in reducing inflammation.
Nootropic Effect
Studies have suggested a potential neuroprotective action of long-term assumption of theobromine through a reduction of Aβ amyloid pathology, which is commonly observed in Alzheimer’s disease patients’ brains. However, Theobromine’s effect on cognitive modulation is still under-explored and would benefit from additional study.
Diuretic Effect
This compound is a natural diuretic that can help increase the amount of urine made by the kidneys, which means it may help reduce water retention and treat edema (fluid buildup).
Sleep Quality
Cocoa is viewed as having a beneficial effect on sleep due to the theobromine content of cocoa. Unlike caffeine, theobromine is less likely to contribute to insomnia.
Properties of Theobromine
| Physical Form | Powder |
|---|---|
| Color | White |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Shelf Life | 24.00 months or longer if stored properly |
| Molecular Weight | 180.167 g·mol−1 |
| Appearance | Solid white powder |
| pH (saturated aqueous solution) | 5.5-7 |
| Density | 1.524 g/cm |
| Storage Conditions | Store in a cool, dry place in tightly sealed containers, protected from heat and light |
| Melting Point | 357 °C |
| Solubility in water | 500 mg/L (25 °C); 1 g/150ml (Boiling water) |
| Refractive Index | 1.6700 |
| Claims (Product Specific) | Naturally Derived, Halal, Kosher, Organic, Non-GMO |
| Biological Activity | Human bodies contain adenosine receptors, which regulate the release of neurotransmitters, oxygen, and blood flow in the heart. Xanthines, including theobromine, are “adenosine antagonists.” They bind to the receptor and block their functioning rather than activating them. Theobromine, like caffeine and the bronchodilator theophylline, may be used as a CNS stimulant, mild diuretic, and respiratory stimulant. |
Typical Formulations
Ice Cream Mix
Here is an example of an ice cream mix formulation table along with the % weight of ingredients:
| Ingredient | Amount (wt %) |
| Cocoa Powder 10/12 | 12 |
| Butterfat | 8 |
| Glucose Syrup 63DE 78% Solids | 5 |
| Sucrose | 1 1.0 |
| Skim Milk Powder | 9.5 |
| Stabilizer | 0.156 |
| Emulsifier | 0.3 |
| Theobromine | Adjusted to 400-700 mg/100 g of product |
| Water | To 100 |
Candy Coating
Here is an example of a candy coating formulation table along with the % weight of ingredients:
| Ingredient | Amount (wt%) |
| Sucrose | 34.4 |
| Cocoa Butter | 11.1 |
| Butter Oil | 10.6 |
| Cocoa Mass | 28.5 |
| Soya Lecithin | 0.43 |
| Cocoa Nibs | 15 |
| Theobromine | 0.4 |
Source: European Patent Office
Theobromine Formulation Considerations
| Physical Form | Powder |
| Stability | Heat Stable (Degradation Temperature 325 °C [2])Light Stable (Not susceptible to photolysis by sunlight)Oxidation Stable |
| Nutritional Profile | No calorific value |
| Sensory Attributes | Bitter taste, odorless |
| Dosage | The dosage of theobromine in food products for flavoring purposes may range from 0.05% to 0.5%. |
| Interaction with Other Components | Theobromine forms salts, which are decomposed by water, and compounds with bases, which are more stable. |
| Absorption & Kinetics | Readily absorbed from the gastrointestinal tract and widely distributed throughout the body. Metabolized in the liver and undergo enterohepatic recycling. |
Safety & Regulatory Considerations
Theobromine is safe when used in appropriate dosages. However, long-term daily intake of up to 1,500 mg may cause the following side effects in some people.
- Nausea
- Loss of appetite
- Headaches
- Negative mood changes
When formulating a product with caffeine and theobromine, the combination may cause an increase in heart rate, alertness, and widening of blood vessels more than either substance would if taken individually.
Animals like dogs metabolize theobromine more slowly than humans and may succumb to theobromine poisoning. For this reason, it’s essential to keep food products containing theobromine away from animals.
Identification Numbers
| Chemical Name | Dimethylxanthine3,7-Dihydro-3,7-dimethyl-1H-purine-2,6-dione |
| CAS Number | 83–67–0 |
| EC Number | 201-494-2 |
| FEMA Number | 3591 |
Acceptable Limits or Maximum Usage
The maximum usage level of theobromine in the food industry, as per FEMA, is as follows:
| Category | Usage Level |
| Baked Goods | 1050 ppm |
| Confectionery/ Frosting | 4000 ppm |
| Gelatine/ Pudding | 795 ppm |
| Milk Products | 990 ppm |
| Soft Candy | 4020 ppm |
| Sweet Sauces | 3300 ppm |
Source: FEMA
Fun Facts About Theobromine
- Theobroma, in Greek, roughly means “food of the gods.”
- Similarly to caffeine and theophylline, Theobromine is a xanthine alkaloid and a methylxanthine. However, it differs from them because it has little stimulatory action on the central nervous system.
Additional Resources
- FDA – Guidance for Industry: Bottled Water and Vending Machines
- PubChem – Theobromine
- FEMA Flavor Ingredient Library – GRAS Substances (3526-3596)
- NCBI Bookshelf – Theobromine
- Google Patents – WO2009089677A1 – Production of Theobromine
- ChemicalBook – Theobromine
- FDA – Substances Added to Food Inventory (theobromine)
- Britannica – Theobromine




