Malic acid is an alpha hydroxy acid (AHA) comprising two carboxylic acid groups and one hydroxyl group. It has a tart, sour taste and occurs naturally in certain fruits and wines. It’s used as an additive in the food and beverage industry for various purposes, including flavor enhancement, preservation, and acidity adjustment.
What is Malic Acid?
Malic acid is a dicarboxylic acid with the chemical formula C4H6O5. It occurs in living organisms as a metabolite in the Krebs cycle and in certain plants for photosynthesis, plant development, and stress responses. L-Malic acid is an essential intermediate of cell metabolism.
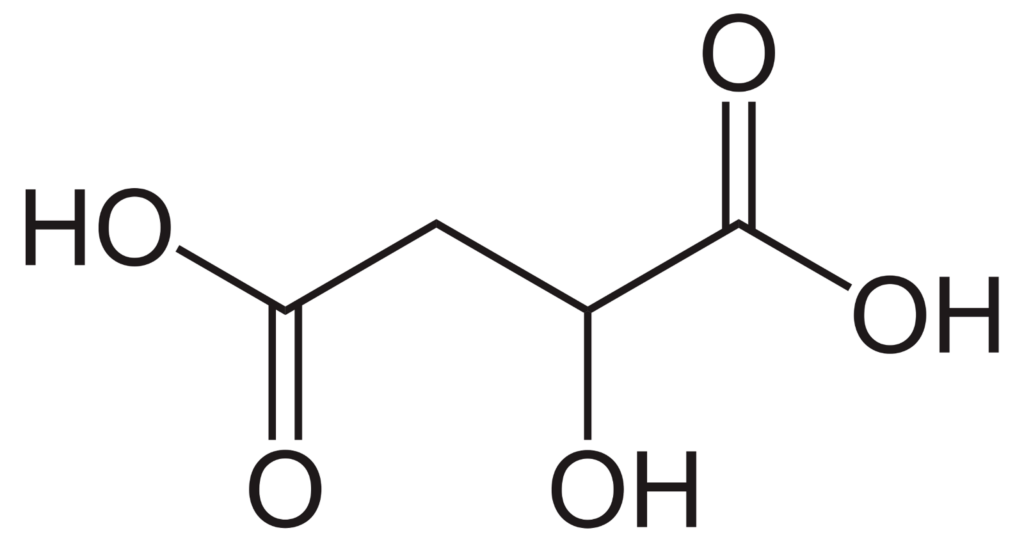
Source: Wikipedia
How is Malic Acid Produced?
Malic acid is found in many fruits and vegetables, including apples, pears, tomatoes, and grapes. It is also found in some alcoholic beverages, such as wine.
Malic acid can be made synthetically through the chemical hydration of maleic or fumaric acid at high temperatures (180–220 °C) and high pressure (14–18 bar), yielding a racemic mixture of dl-malic acid. The biosynthesis of l-malic acid from carbohydrates (glucose) involves the carboxylation of pyruvic acid, which leads to oxaloacetic acid that is reduced to l-malic acid.
Malic acid is commercially produced via large-scale fermentation using microorganisms with high fumarase (fumarate hydratase) activity. Gene promoters can amplify the enzyme for maximal malic acid production. Various agricultural residues can be used after treatment as a substrate for the fermentation malic acid.
Applications in the Food and Beverage Industry
Malic acid is a multipurpose food additive with various applications in the food and beverage industry. Many of these applications are described in the table below.
| Function | Applications |
| Acidulant | It Imparts sour taste. Reduces pH. |
| Flavoring Agent | Enhances fruit flavors. Masks off-notes from saltsProvides lingering sourness. It imparts a sour taste compared to citric acid. |
| Preservative | Improves shelf life. Antimicrobial activity |
| Flavor Enhancer | Works in harmony with artificial sweetenersMasks aftertaste of sweeteners |
| Raising Agent | Enhances gelling properties improves pectin gel structure |
| Sequestrant | Potent antioxidant capacity. It helps in retaining color. |
| Gelling Aid | Enhances gelling properties and improves pectin gel structure |
Product Examples
Malic acid is used in various products, as described in the table below.
| Category | Examples |
| Beverages | Carbonated Beverages, Still Beverages, Milk-Based Beverages, Fruit Juices |
| Confectionery | Candies, Chewing Gums, Soft Chews, Hard-Boiled Candies |
| Convenience Foods | Powdered Beverages, Powder Mixes |
| Fruit Preparations and Preserves | Jams, Jellies, Marmalades |
| Bakery | Cake, Cookies Snack Bars, Pies |
| Alcoholic Beverages | Wine |
| Desserts | Gelled Desserts, Cream-Based Desserts |
Properties of Malic Acid
| Physical Form | Crystalline powder or granules |
| Color | Colorless to white |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Molar Mass | 134.09 g/mol |
| Melting Point | 130 °C |
| Density | 1.609 g/cm 3 |
| Solubility | 558 g/L (at 20 °C) |
| Molar enthalpy of solution (298.15 K, 0.0318 mol · kg -1) | 21846 ± 86 J · mol−1 |
| pKa | pKa1 = 3.40pKa2 = 5.20 |
| pH (1% aqueous) | 2.34 |
| Vapor Pressure | 0.00000293 mmHg |
Typical Formulations
Pectin Jelly
Malic acid is used as a delayed-action or time-release acidulant in the formulation of jelly to use pectin in a delayed gelation process efficiently. By enabling the optimum gelling pH, desired gel strength can be achieved with minimal quantities of pectin. A formulation example is provided below.
| Phase | Ingredient | Composition |
| Pectin Blend | Sucrose | 30 g |
| Pectin (slow set” high methoxy pectin- 62 to 65 DM) | 4 g | |
| Sodium citrate | 1.0 | |
| Malic acid | 0.75 | |
| Water | 50 ml | |
| Sugar Syrup | Sucrose | 120 g |
| Corn syrup (80) | 100 | |
| Water | 50 ml |
Source: Google Patents
Effervescent Tablet
Malic acid is used as an effervescence agent and baking soda in the formulation of tablets to prepare drinks with prolonged gas evolution.
| Ingredient | Composition |
| Baking soda | 35-45% |
| Malic acid | 30-40% |
| Sorbitol | 8-17% |
| Flavor | 5% |
Source: Google Patents
Fruit Cake
A typical formulation example of fruit cake with malic acid is given in the table below.
| Ingredient | Composition |
| Blueberry (Pulp) | 100-120 g |
| Carrageenan | 6-10 g |
| Sugar | 40-50 g |
| Maltose | 20-30 g |
| Citric acid | 0.5-2 g |
| Malic acid | 0.5-1 g |
| Potassium sorbate | 0.5-2 g |
Source: Google Patents
Comparison with Other Acidulants
Malic acid has a high acidity (sour acidity is 20% stronger than citric acid) but a soft taste.
Here is the relative sourness, in arbitrary units, of malic and other organic acids compared to other common acidulants:
- Glucono-delta-lactone: 310
- Lactic acid: 107
- Citric acid: 100
- Succinic acid: 87
- Malic acid: 75
- Tartaric acid: 70
- Fumaric acid: 55
Malic Acid Formulation Considerations
When compared to other organic acids, malic acid has many advantages. Its sour tanginess increases at lower pH levels. Acidic foods with malic acid will have a more pungent tang. And malic acid dissolves rapidly, making it highly useful in powdered mixes. It stabilizes color and chelates metal ions.
| Physical Forms | Colorless to white crystalline powder or granules |
| Effect on Shelf Stability of Food Products | Much like salt, malic acid intensifies the flavor and melds different flavors within one product to create a more rounded taste experience. Malic acid accounts for the memorable aftertaste in some confectionery items. L-malic acid taste is similar to the sour taste of natural apples, with high acidity, soft taste, and it stays longer on the palate. L-malic acid can be used as a color-retention agent for some foods. It is also used as a deodorant to remove unpleasant odors. |
| Sensory Attributes | Much like salt, malic acid intensifies the flavor and melds different flavors within one product to create a more rounded taste experience. Malic acid accounts for the memorable aftertaste in some confectionery items. L-malic acid taste is similar to the sour taste of natural apples, with high acidity soft taste, and stays longer on the palate. L-malic acid can be used as a color-retention agent for some foods. It is also used as a deodorant to remove unpleasant odors. |
Acetic acid is another organic acid commonly found in various food products.
Safety & Regulatory Considerations
| FDA Information | Malic acid is listed in the food additives with the number E 296. Per the EU, malic acid “shall be used in accordance with good manufacturing practice, at a level not higher than is necessary to achieve the intended purpose and provided the consumer is not misled.” |
| EU Information | Malic acid is listed in the food additives with the number E 296. Per the EU, malic acid “shall be used following good manufacturing practice, at a level not higher than is necessary to achieve the intended purpose and provided the consumer is not misled.” |
Identification Numbers
| CAS Number | 6915-15-7 |
| EC Number | 230-022-8 |
| E No. (Food Additive) | 296 |
| INS No. (Food Additive) | INS 296 |
Acceptable Limits or Maximum Usage
The maximum limit of malic acid usage has been defined by FDA as follows.
| Category | Maximum Level |
| Non-alcoholic beverages | 3.4% |
| Chewing gum | 3.0% |
| Gelatines, puddings, fillings | 0.8% |
| Hard candy | 6.9% |
| Jams & jellies | 2.6% |
| Processed fruits and fruit | 3.5% |
| Soft candy | 3.0% |
| All other food categories | 0.7% |
Fun Facts About Malic Acid
- Chemist Antoine Lavoisier named malic acid “acide malique” because of its similarity to a sour apple flavor.
- When applied to the skin, malic acid is used in skin care products to clear away dead skin cells.
Additional Resources
- Malic Acid and Its Potential Benefits – NCBI (PMC)
- Malic Acid – ScienceDirect – Topics in Biochemistry, Genetics, and Molecular Biology
- Metabolic Engineering of Malic Acid Production – Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology
- Malic Acid – Bakerpedia
- Benefits of Using Malic Acid in Food Production – Bell Chem
- Subpart B – Listing of Specific Substances Affirmed as GRAS – Code of Federal Regulations
- Malic Acid – WHO Food Additives and Contaminants JECFA Database
- Commission Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 – Annex III, Part B – European Union Law
- Official Journal of the European Union – Regulation (EU) No 231/2012 – PDF
- Malic Acid – ScienceDirect – Reference Module in Food Science











