Sodium acetate is the salt form of acetic acid. It’s a multipurpose additive commonly used in the food and beverage industry as a flavoring agent, preservative, pH control agent, sequestrant, and buffering agent.
What is Sodium Acetate?
Sodium acetate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula NaCH3CO2, abbreviated as NaOAc. It is a salt composed of sodium cations (Na+) and acetate anions (CH3CO2-). It can also be called “dry acetic acid” as it is composed of free acetic acid in a solid form (39 to 41%). The crystal structure of anhydrous sodium acetate has been described as alternating sodium-carboxylate and methyl group layers.
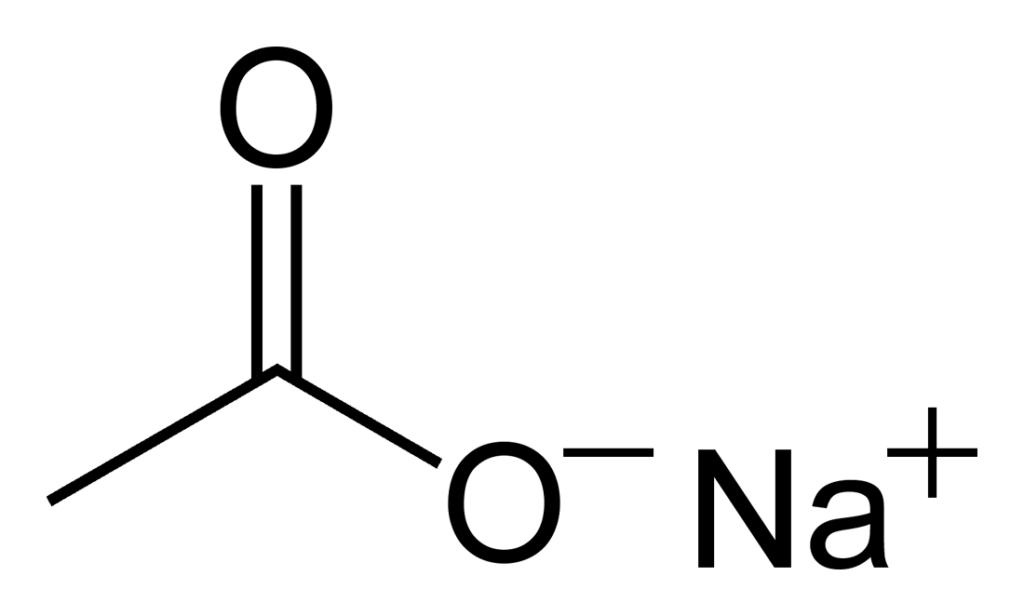
Source: Wikipedia
How is Sodium Acetate Produced?
Sodium acetate is the salt of acetic acid. It is formed by the reaction of acetic acid with sodium carbonate, an exothermic reaction that generates heat that evaporates the moisture produced.
Use of Sodium Acetate in Food & Beverage Products
Sodium acetate eliminates unwanted changes in food products’ taste, color, and texture. It complexes with unwanted metal ions, stabilizing the food against loss of quality. It also softens water used for production in the food industry.
Applications in Food & Beverage Products
Sodium acetate is a multipurpose food additive. Its functions include the following:
| Function | Applications |
| Flavoring Agent | Adds a slightly salty and sour flavor to food |
| Preservative | Preserves food by inhibiting the growth of bacteria |
| Acidity Regulator (pH control Agent) | Creates a slight increase in the pH |
| Sequestrant | Used to sequester polyvalent metal ions |
| Buffering Agent | Prevents the pH of a solution from changing drastically through interactions with acids or bases |
Product Examples
| Type | Examples |
| Convenience | Processed Cereals, Soup Mixes, Marinades, Steamed Fish & Vegetables |
| Savory Foods | Curries, Curry Mixes, Sauces |
| Confectionery | Jams, Jelly, Marmalades |
| Bakery | Bread |
| Processed Foods | Croquette, Hamburger Patty, Meatball, Dumpling |
Properties of Sodium Acetate
| Physical Form | Powder |
| Color | White to colorless |
| Odor | Vinegar (acetic acid) odor |
| Storage Temperature & Conditions | Store in a dry place, separated from strong acids and strong oxidants. |
| Appearance | White deliquescent powder |
| pH (1 % Aqueous ) | 8.0 – 9.5 |
| Density @ 20°C | 1.528 g/cm3 |
| Molar Mass | 82.034 g·mol−1 |
| Melting Point | 324 °C (anhydrous) |
| Refractive Index | 1.464 |
| Solubility @ 20°C | Anhydrous: 123.3 g/100 mL & Trihydrate: 46.4 g/100 mL |
| pKa | 4.75 |
Typical Formulations
Bread
Here is an example of a bread formulation table with sodium acetate along with the weight of ingredients:
| Ingredient | Composition |
| Wheat Flour | 400 g |
| Shortening | 16 g |
| Yeast | 8 g |
| Common Salt | 7.2 g |
| Sugar | 16 g |
| Fermentation Accelerator | 0.8 g |
| Sodium Acetate | 0.3 % |
| Fumaric Acid (Coated) | 0.2 % |
Source: Google Patents
Low Methyl Pectin Jelly
Here is an example of a pectin jelly formulation table with sodium acetate along with the weight of ingredients:
| Ingredient | Composition |
| Commercial Low Methyl Pectin | 6.7 g |
| Cane Sugar | 80 g |
| Distilled Water | 240 g |
| Vanilla Flavoring | 1 ml |
| Yellow Color | 0.7 ml |
| Sodium Acetate (1% Aqueous) | 7 ml (to adjust the pH to 4.0) |
Source: Google Patents
Sodium Acetate Formulation Considerations
| Physical Forms | Powder |
| Stability | Heat: Stable until around 380 °CpH: StableOxidation: Stable |
| Sensory Attributes | Slightly sour to salty taste |
| Dosage | 0.05-0.5 or more, depending on the application |
Safety & Regulatory Considerations
| FDA Information | Sodium acetate is regulated as Generally Recognized as Safe (GRAS) by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). It is allowed as a food additive in the US and may be found in certain food items as a flavoring agent, adjuvant, and pH control agent. |
| EU Information | Sodium acetate is listed as a permitted food additive by the EU under number E 262. It is allowed to be used in the following categories at level “quantum satis:” 4.2.3: Canned or bottled fruit and vegetables, 7.1.1: Bread, 7.1.2: Pain courant francais, 13.1.3: Processed cereal-based foods and baby foods for infants, 8.2: Meat preparations |
Safety & Toxicity of Sodium Acetate
Sodium acetate is irritating to the mucous membranes and upper respiratory tract. It may be harmful by inhalation, ingestion, or skin absorption. It may cause eye, skin, or respiratory system irritation. The toxicological properties of this compound have yet to be fully evaluated.
Oral LD50 for rats was reported to be 3530mg/kg, a significantly high number. For this reason, sodium acetate is less likely to be hazardous for human beings, provided the intake is within range.
Identification Numbers
| Chemical Name | Sodium acetate |
| CAS Number | 127-09-3 |
| EC Number | 204-823-8 |
| E Number (Food Additive) | E 262 |
| INS No. (Food Additive) | INS 262 |
| FEMA Number | 3024 |
Acceptable Limits or Maximum Usage
- The ADI for sodium acetate is set to “not limited” by the WHO.
- The maximum usage level of sodium acetate in the food industry per the FDA is as follows:
| Category | Maximum Usage (%) |
| Breakfast Cereals | 0.007 |
| Fats & Oils | 0.5 |
| Grain Products & Pasta | 0.6 |
| Hard Candy | 0.15 |
| Jams & Jellies | 0.12 |
| Soft Candy | 0.2 |
| Soups & Soup Mixes | 0.05 |
| Sweet Sauces | 0.05 |
Fun Facts About Sodium Acetate
- Sodium acetate can form beautiful crystals known as “hot ice” when a supersaturated solution is cooled. These crystals can be formed by heating a solution of sodium acetate trihydrate and then allowing it to cool slowly.
- Sodium acetate is used in commercial hand warmers as it can generate heat when it undergoes a phase change from a supersaturated solution to a solid.
Additional Resources
- Bell Chem – Industrial Uses of Sodium Acetate
- Infinity Learn – Sodium Acetate
- ResearchGate – Quality and Hygiene of Beef Burgers in Relation to the Addition of Sodium Ascorbate, Sodium Citrate, and Sodium Acetate
- NCBI – Sodium Acetate in Analytical Chemistry
- ScienceDirect – Sodium Acetate as a Novel Catalytic Reaction Medium for the Synthesis of Furo[3,4-b]quinoline Derivatives






