Sodium hyaluronate (a derivative of hyaluronic acid) is ideal for moisture management since it acts as a water reservoir in the cells. As a result, sodium hyaluronate is popular with product formulators in the personal care industries.
What is Sodium Hyaluronate?
Sodium hyaluronate is a water-soluble salt obtained from hyaluronic acid (HA). Hyaluronic acid is a polyanionic polysaccharide, naturally present in connective tissues as a compound with protein. With chondroitin sulfate, HA fills the intercellular gap to maintain tissue structure and retain moisture, lubricability, and tissue flexibility. It also serves to protect the tissue from bacterial infection. Because of its unique rheological, viscoelastic, and hygroscopic properties, HA plays a key role in protecting and stabilizing the skin at the cellular level.
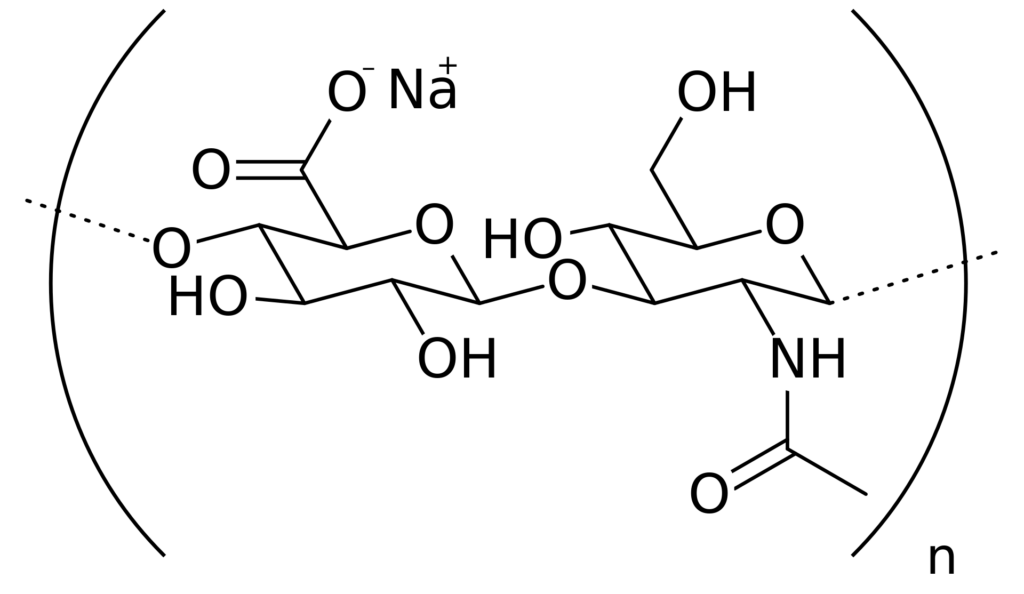
What is the Difference Between Sodium Hyaluronate and Hyaluronic Acid?
Native Hyaluronic Acid suffers from its low resistance to some extreme conditions, which results in its limitations in practical usage in formulations. For this reason, chemical modifications of HA are intended for cosmetic or pharmaceutical applications. Chemically modified HA derivatives such as Sodium Hyaluronate are usually more mechanically robust, as such, they are more suitable for final products manufactured using higher temperatures, pressures, or shear stress. Sodium Hyaluronate usually has a stronger binding capacity to the skin, and as a result, they are not washed off easily compared to unmodified Hyaluronic acid. Therefore like Hyaluronic acid, Sodium hyaluronate is incredibly hydrating, but it has specific properties that make it more attractive to product formulators. Sodium hyaluronate can penetrate deeper into the skin and is more stable.
How does sodium hyaluronate work?
As a polymer, hyaluronic acid comprises long, complicated chain-like molecules that allow other chemical compounds to bind (including water). HA is also capable of attaching to other cells. Sodium hyaluronate works as a humectant by pulling in moisture from the environment and from the skin’s underlying layers into the epidermis.
How is sodium hyaluronate produced?
Sodium hyaluronate has traditionally been produced by extracting hyaluronic acid from animal tissues or using bacterial expression systems in Streptococci. Today, manufacturers have developed alternative vegan sources, including endotoxin-free microorganisms.
Applications for Skin Care and Hair Care Products
The properties of hyaluronic acid make it beneficial to the body in various ways. Here are seven reasons sodium hyaluronate is useful in personal care products.
Humectancy
Sodium hyaluronate deeply hydrates the skin, making it more supple thanks to its water-binding capability. It creates a barrier on the skin’s surface, providing vital skin lubrication.
Flexibility
Like collagen, sodium hyaluronate makes the skin more supple and flexible, making it popular in products designed to improve the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles. Because of its low molecular weight compared to hyaluronic acid, it can penetrate the skin more deeply. Additionally, it’s active in cellular renewal, aiding in repairing and promoting cell multiplication. For this reason, it’s commonly used as an active ingredient in dermal fillers.
Moisturizing Capability
Sodium hyaluronate aids in repairing a compromised moisture barrier in the skin. Maintaining a healthy skin barrier is vital to prevent transepidermal water loss (TEWL), which can lead to inflammatory conditions, and to help keep skin hydrated and flake-free. Sodium hyaluronate has a lightweight feel and imparts a dewy finish without leaving a thick, greasy residue.
Non-Acnegenic
Topical application of sodium hyaluronate often improves breakout-prone skin and is thought to improve acne by rebalancing the skin. It’s generally considered to be non-comedogenic, which means it won’t clog pores.
Protection Against Environmental Stressors
Sodium hyaluronate defends hair shafts against harmful environmental stressors such as UV rays and helps restore scalp moisture balance. Additionally, sodium hyaluronate helps to stimulate hair growth, aids in exfoliation and promotes resilience and softness in weak hair strands.
Product Examples
odium Hyaluronate has a broad range of applications in personal care products, making it one of the most common active ingredients in skin care, hair care, and cosmetics. Here are a few examples.
| Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Skin Care Products | Cleansers, moisturizers, creams, serums, and products designed to increase hydration, support the skin barrier, and relieve dry skin types |
| Anti-Aging Products | Serums, creams, and lotions designed to reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles |
| Cosmetics | – Toners, astringents, and makeup removers – Color cosmetics such as foundation and concealer that combine skincare benefits with makeup |
| Hair Care Products | Hair serums, hydrating hair gels, and hair masks to improve the condition of the hair |
Properties of Sodium Hyaluronate
Sodium hyaluronate is a physiological glycosaminoglycan with hydrating, regenerative, and protective effects. Here are its fundamental properties.
| Appearance | White or Off-White Powder |
| Odour | Odorless |
| pH (0.1% water solution) | 5.5-7.5 |
| Solubility | Water Soluble |
| Purity (varies as per grade) | 93-99% |
| Molecular weight (kDa) | Typically between 150-1300 |
| Transparency | 98%(0.1% Solution) |
| Loss on Drying | < 10% |
| Shelf Life | Varies from 24 months-36 months |
Typical Formulations
Supercharged Night Booster With Niacinamide PC and HYALURONIC ACID-BT
This serum supports skin cells’ natural overnight repairing process, helping reduce and prevent premature stress-induced signs of aging, for renewed skin vibrancy.
Here is an example of a serum formulation table with sodium hyaluronate along with the phases and % weight of ingredients:
| Phase | INCI Name | % w/w |
|---|---|---|
| A | – Aqua – Betaine – Disodium EDTA – Cellulose Gum – Glycerin – PEG/PPG-17/6 Copolymer – Chondrus Crispus Extract – Butylene Glycol – Sodium Hyaluronate – Carbomer – Phenoxyethanol, Ethylhexylglycerin | 80.11 2.00 0.02 0.10 2.00 1.00 0.30 2.00 1.02 0.22 0.50 |
| B | – Alcohol Denat, Aqua – PEG-60 Hydrogenated Castor oil – Parfum – Potassium Hydroxide – Bis-PEG-18-Methyl Ether Dimethyl Silane | 3.00 0.20 0.05 0.09 0.40 |
| C | Niacinamide | 7.00 |
Sodium Hyaluronate Formulation Considerations
Sodium hyaluronate is typically used at a level of 0.5 – 2% and can safely be heated up to 60℃. It should be presoaked / pre-dissolved (0.5%/10 ml water recommended) to form a uniform gel solution to avoid lump formation. It’s vital to take sanitary precautions while working with sodium hyaluronate since it has a high risk of contamination once dissolved.
Chemists recommend using phenoxyethanol as the basic preservative system with ethylhexylglycerin as a preservative booster. Parabens should be avoided as they can result in irritation and allergic reactions.
Sodium Hyaluronate Safety & Regulatory Considerations
The FDA has approved sodium hyaluronate for:
- Sodium Hyaluronate is approved by US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) as a topical product for use in cosmetics and personal care applications.
- A monograph characterizing sodium hyaluronate produced from microbial fermentation (specifies Streptococcus) was published in the Food Chemical Codex (11th ed.) (Food Chemicals Codex, 2018).
- A monograph for HA (including NaHA) is also included in the Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database (Therapeutic Research Faculty, 2018).
- Japan: HA was deemed safe for food use and was subsequently listed in the Japanese Food Additives Catalog (Japanese Ministry of Health Labour and Welfare, 1996).
Safety Information
From a toxicity standpoint, sodium hyaluronate is considered non-toxic. When used topically, there are usually no side effects. However, because sensitivity to any ingredient is possible, a patch test should be done before full usage.
Sodium hyaluronate is non-comedogenic and does not clog pores or cause breakouts. Additionally, when extracted from vegetable sources, sodium hyaluronate is vegan.
Fun Facts About Sodium Hyaluronate
- Sodium hyaluronate appears naturally in the body, including in eyes, joints, and skin.
- The first scientific study involving hyaluronic acid was done in 1880. The French scientist Portes observed the unique properties of mucoids in the cornea and cartilage and called it “hyalomucine.”
- Because sodium hyaluronate works by trapping water molecules, it’s ideal for all skin types. It’s commonly used in gel serums designed for oily skin that can’t tolerate heavy moisturizers.




