The name “Oleic Acid” is derived from the Latin word oleum, which means oil. In this article, we’ll look at the role of oleic acid in the formulation of cosmetics and personal care products.
What is Oleic Acid?
In chemical terms, oleic acid is classified as a monounsaturated omega-9 fatty acid, abbreviated with a lipid number of 18:1 cis-9, and is a main product of Δ9 desaturase. Its formula is CH3−(CH2)7−CH=CH−(CH2)7−COOH. The salts and esters of oleic acid are called oleates.
The hydrolysis of various animal and vegetable fats and oils obtains oleic acid. Oleic acid biosynthesis involves the action of the enzyme stearoyl-CoA 9-desaturase acting on stearoyl-CoA. Stearic acid is dehydrogenated to give the monounsaturated fatty acid derivative, oleic acid.
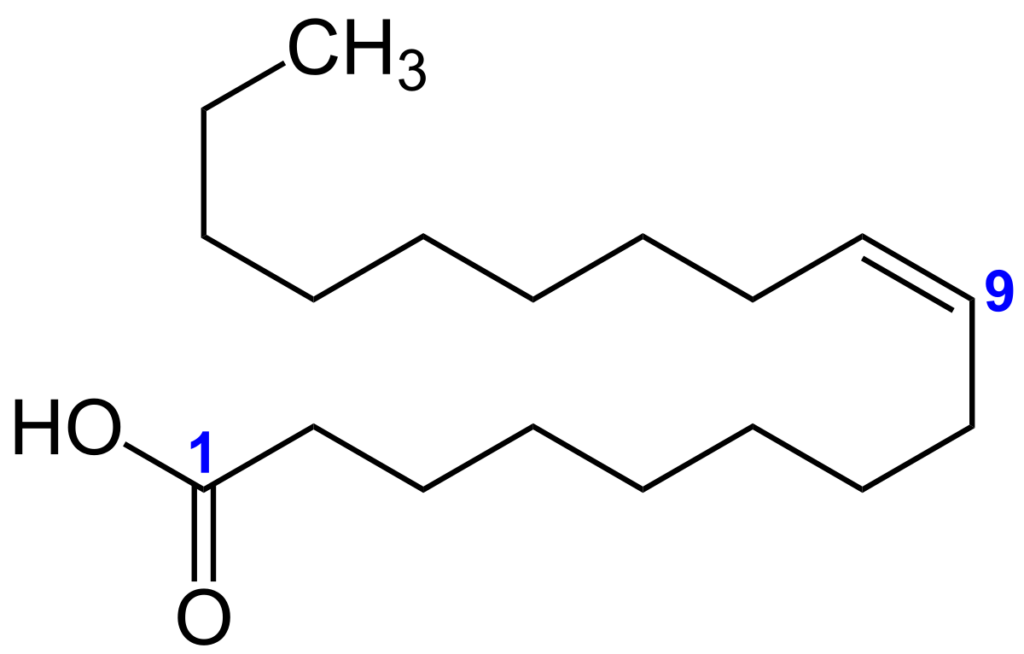
Oleic acid chemical structure. Source: Wikidata
Fatty acids (and their salts) typically do not occur as such in biological systems. Instead, they occur in their ester forms. Oleic acid is found in fats (triglycerides), the phospholipids that make membranes, cholesterol esters, and wax esters.
Oleic acid triglycerides make up about 70% of olive oil. They comprise 59-75% of pecan oil, 61% of canola oil, 36-67% of peanut oil, 60% of macadamia oil, 20-80% of sunflower oil, and 40% of sesame oil. Oleic acid is abundant in many animal fats, constituting 37- 56% of chicken and turkey fat and 44-47% of lard.
Use of Oleic Acid in Cosmetics and Personal Care
Oleic acid has a wide variety of applications in cosmetics and personal care. Here are a few of its uses.
Emollients: Essential fatty acids, including oleic acid, influence skin physiology via their effects on skin barrier functions, membrane fluidity, and cell signaling. Emollients are designed to plasticize, soften, and smooth the skin, usually by filling the void between the corneocytes and replacing the lost lipids in the Stratum Corneum. Additionally, emollients can provide protection and lubrication on the skin surface to minimize chafing and enhance the skin’s aesthetic smoothness and softness. Oleic acid can also improve a product’s skin penetration abilities.
Emulsifiers: Emulsifiers are a core component of many personal care products since most moisturizing, nourishing, and protective formulations are emulsions. Emulsifier selection is crucial for the stability of an emulsion and significantly impacts the final formulation’s consistency and viscosity, color, odor, and functional properties. Oleic acid is commonly used as an emulsifier along with other co-emulsifiers.
Moisturizers: Combining oleic acid with other lipids (fats) boosts its skin-calming ability, making oleic acid helpful in reducing signs of dryness and sensitivity when used in this capacity.
Soap Formation: Oleic acid reacts with alkalis to form soaps.
Product Examples
| Type | Examples |
| Skin Care | Face Creams, Body Lotions, Soaps, Body Butters |
| Hair Care | Conditioners, Nourishing Hair Masks, Serums, Shampoos |
| Color Cosmetics | Lipsticks, Lip Balm, Foundation, Eye Shadow, Mascara |
| Bath & Body | Soap, Moisturizing Body Wash, Foaming Body Cleansers |
| Baby Care | Baby Oils, Lotions, Creams, Mild Baby Shampoo |
| Skin Cleansers | Make-Up Remover, Micellar Skin Cleansers |
Properties of Oleic Acid
| Appearance at 25 °C | Pure oleic acid is a colorless to pale yellow, oily liquid at temperatures above 5-7°C. |
| Molecular Weight (g/mol) | 282.468 |
| Density at 25°C | 0.895 g/mL |
| Specific Gravity | 0.892 (20/4℃) |
| Solubility | Water insoluble, soluble in ethanol |
| Melting Point | 13 to 14°C |
| Boiling Point | 360°C |
| Saponification Value | 196-206 |
| Acid Value | 198-207 |
| Odor | Lard-like odor |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, aluminum. |
| Shelf Life | 12-18 months |
| Storage Conditions | On exposure to air, oleic acid gradually absorbs oxygen, darkens in color, and develops a more pronounced odor. At atmospheric pressure, it decomposes when heated at 80–100°C.Oleic acid should be stored in a well-filled, well-closed container, protected from light, in a cool, dry place.Ideal storage temperature: -20°C |
Oleic Acid Formulation Considerations
- Oleic acid is highly compatible with mineral oils, fats, and other plant derived oils.
- Always add oleic acid in the oil phase of manufacture. The pH range to be considered when formulating with Oleic acid is 8-9.
Typical Formulations
Body Wash
In body wash, the combination of other neutralized fatty acids with oleic acid creates a dense, smooth foam which leaves the skin feeling moisturized, luxurious, and clean.
| PHASE | INCI Name | Trade Name | % Wt. |
| A | Propylene Glycol | Propylene Glycol USP/EP | 10.00 |
| Lauric Acid | NAA®-122 | 7.00 | |
| Myristic Acid | NAA®-142 | 3.00 | |
| Palmitic Acid | NAA®-160 | 1.00 | |
| Oleic Acid | Oleic Acid P | 1.00 | |
| Deionized Water | Water | 12.00 | |
| B | Potassium Hydroxide (85%) | Potassium Hydroxide | 3.50 |
| Deionized Water | Water | 5.00 | |
| Deionized Water | Water | 2.00 | |
| C | Cocamide DEA (and) Diethanolamine | Tohol N-220XM | 5.00 |
| Sodium Laureth Sulfate | Alscop NS-230 | 4.00 | |
| Cocamidopropyl Betaine | Obazolin CAB-30 | 6.00 | |
| Glycol Distearate | Emanon® 3201-M | 1.00 | |
| D | Water | Deionized Water | 15.00 |
| Tetrasodium EDTA | Chelest 2D-SD | 0.01 | |
| Acrylates Copolymer | Carbopol® Aqua SF-1 Polymer | 13.00 | |
| E | Hydrolyzed Jojoba Esters (and) Water (Aqua) | Floraesters K-20W Jojoba | 3.00 |
| Water | Deionized Water | 4.00 | |
| Potassium Hydroxide | Potassium Hydroxide (85%) | 0.80 | |
| Water | Deionized Water | 2.09 | |
| F | Parfum | Fragrance | q.s |
| Total | 100 | ||
Formulation Procedure
- Heat the Propylene Glycol, USP/EP to 65-70°C with stirring. Add the remaining ingredients of Phase A in the order listed with stirring until fully dissolved.
- Dissolve the Potassium Hydroxide (85%) in the first deionized water listed in Phase B. Slowly add this solution to Phase A at 70-75°C with stirring to neutralize the fatty acids. Rinse the container with the deionized water listed in Phase B. Add the ingredients of Phase C in the order listed to Phase AB at 60-65°C.
- Create a pre-mix of Phase D by adding the ingredients in the order listed. Slowly add Phase D to Phase ABC. Allow mixing time for the polymer to disperse completely in the solution.
- Mix the Floraesters K-20W Jojoba in the first deionized water listed in Phase E. Add this pre-mix slowly to Phase ABCD at a mix temperature of 60-65°C. Pre-mix the Potassium Hydroxide (85%) in the second deionized water listed in Phase E. Use this pre-mix to neutralize the Carbopol Aqua SF-1 Polymer by slowly adding it to Phase ABCD. Use the final deionized water listed in Phase E to rinse the neutralization containers into Phase ABCD.
- Add the fragrance of Phase F to Phase ABCDE at a mix temperature of 60-65°C. Use the deionized water listed in Phase F to bring the batch weight up to the 100% theoretical weight at this point in the procedure.
- Cool the batch to room temperature. Determine the pH and viscosity of the batch.
Oleic Acid Safety & Regulatory Concerns
FDA Information: GRAS-listed and included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (inhalation and nasal aerosols, tablets, topical and transdermal preparations)
Canadian Information: Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients.
EU Information: Included in nonparenteral medicines (metered dose inhalers; oral capsules; oral prolonged release granules; topical creams and gels) licensed in the UK.
Cosmetic Ingredient Review (CIR) Information: The independent Cosmetic Ingredient Review panel has ruled oleic acid safe as used in cosmetics, where typical usage ranges from 1–10%.
Identification Numbers
| CAS Number | 112-80-1, 67701-08-0 |
| EC Number | 204-007-1 |
| FEMA Number | 2815 |
| ELINCS Number | 204-007-1 |
The maximum usage level of oleic acid in personal care products per the CIR is as follows.
| Ingredient | Ideal % Composition |
| Baby Shampoo | >10% |
| Baby Oils, Lotions | 1-5% |
| Bath Oils, Tablets & Salts | 5-10% |
| Eyeliner, Eyeshadow, Mascara | 0.1-5% |
| Eye-Makeup Remover | 1-5% |
| Hair Masks, Hair Conditioners | 10-25% |
| Shampoos | 8-15% |
| Lipsticks | 5-10% |
| Foundations | 1-5% |
| Nail Base Coats, Undercoats | >10-25% |
| Aftershave Lotions, Creams | 0.1-1% |
| Face, Body, Hand Skin Care Preparations | 1-10% |
Health Effects of Oleic Acid
Skin Irritant: Slight to moderate skin irritation has been observed with use of oleic acid. Oleic acid may cause slight skin edema with long-term use.
Comedogenic: A significant increase in lipid peroxide level of oleic acid was observed after 18 hours of UVA irradiation. The lipid peroxide concentration is positively correlated with the degree of comedo formation. For this reason, oleic acid is classified as highly comedogenic.
Non-Carcinogenic: No evidence of mutagenicity and carcinogenicity has been reported for oleic acid.
Fun Facts About Oleic Acid
- Oleic acid is the most abundant fatty acid in human adipose tissue and the second most abundant in human tissues overall.
- Oils with oleic acid are often used to replace saturated fats in the diet.





