Magnesium carbonate takes the form of light, white friable masses or as a bulky, white powder. It is odorless with a slightly earthy taste. However, since it has a high absorptive ability, it can easily absorb odors. Magnesium carbonate most often appears in its anhydrous salt form. This article will explore how magnesium carbonate is used in cosmetics and personal care products.
What is Magnesium Carbonate?
Magnesium carbonate occurs naturally in the mineral magnesite and is also found in other minerals such as dolomite and calcite.
Magnesium carbonate is not a homogeneous material but may consist of the Normal hydrate, the Basic hydrate, and the Anhydrous material MgCO3, which is rarely encountered. The USP 32 describes magnesium carbonate as either a Basic Hydrated Magnesium Carbonate or a Normal Hydrated Magnesium Carbonate.
The main differences between basic and normal hydrated magnesium carbonate are their chemical formulas and specific uses.
Basic hydrated magnesium carbonate is often used in medical and industrial applications, while normal hydrated magnesium carbonate is more commonly used in consumer products and cosmetics. Basic magnesium carbonate is probably the most common form, and may vary in formula between light magnesium carbonate, (MgCO₃)₃ Mg(OH)₂·3H₂O, and magnesium carbonate hydroxide, (MgCO₃)₄Mg(OH)₂·5H₂O. Normal magnesium carbonate is a hydrous magnesium carbonate with a varying amount of water, MgCO₃·xH₂O.
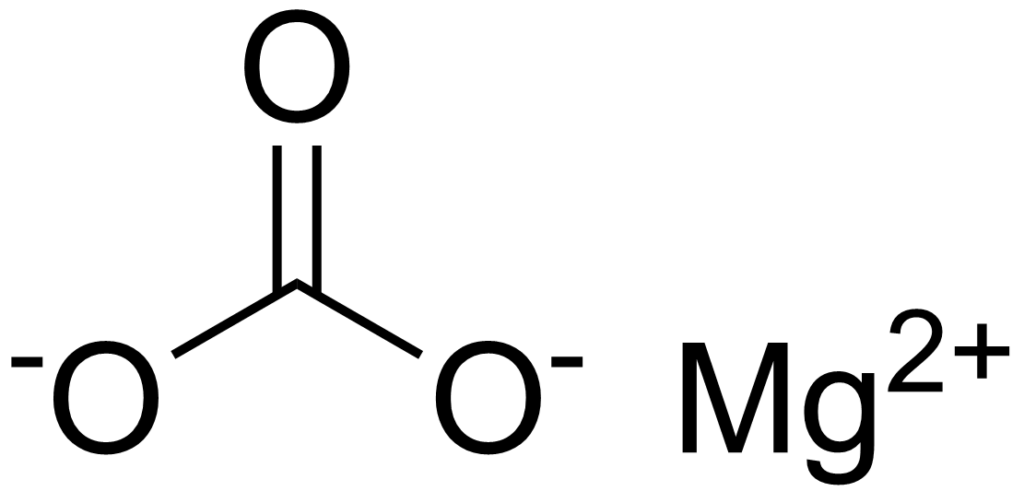
Magnesium carbonate, MgCO₃)₄·Mg(OH)₂·5H₂O, is also known as magnesium carbonate hydroxide. It is a white powder formed either by adding an alkaline carbonate (such as sodium carbonate) to a solution of magnesium sulfate or by carbonation of a slurry of magnesium hydroxide followed by boiling of the resulting magnesium carbonate.
The Pharmacopeia Europe describes magnesium carbonate as being a Hydrated Basic Magnesium Carbonate in two separate monographs:
Heavy Magnesium Carbonate (PhEur 6.5) and Light Magnesium Carbonate (PhEur 6.4)
The molecular formula and molecular weight of heavy magnesium carbonate (tetrahydrate) are [(MgCO₃)₃Mg(OH)₂·4H₂O] and 383.32 g/mol, respectively, while the molecular formula and molecular weight of light magnesium carbonate (trihydrate) are [(MgCO₃)₃ Mg(OH)₂·3H₂O] and 365.30 g/mol, respectively.
Depending upon the manufacturing process used, the composition of the magnesium carbonate obtained may vary from normal hydrated magnesium carbonate to basic hydrated magnesium carbonate.
- Light magnesium carbonate may be manufactured by saturating an aqueous suspension of dolomite, CaMg(CO3)2, with carbon dioxide under pressure. On the increase of the temperature, calcium carbonate precipitates almost entirely. The filtered solution is then heated to boiling; the magnesium bicarbonate in the solution loses carbon dioxide and water, and light magnesium carbonate precipitates. The molecular weight of light magnesium carbonate is 365.30.
- Heavy magnesium carbonate may be manufactured by mixing a hot concentrated solution of magnesium chloride or magnesium sulfate with a solution of sodium carbonate. The heavy magnesium carbonate may be either precipitated to produce a granular material or spray-dried. The molecular weight of heavy magnesium carbonate is 383.32.
Use of Magnesium Carbonate in Cosmetics and Personal Care Products
In cosmetics and personal care products, magnesium carbonate performs the following functions.
- Bulking Agent: Light magnesium carbonate is used to increase fluffiness and aid in fragrance absorption. It also provides a base for the color pigments. It’s frequently used in powders to contribute slip and consistency. And since it’s typically white, it helps to dilute the color. In addition, magnesium carbonate also helps to increase the adhesiveness of facial powders to the skin.
- Mattifying Agent: Magnesium Carbonate has a long-lasting mattifying effect due to its high absorbency. For this reason, it helps reduce shine, giving a velvety finish to color cosmetic applications. It can be used as an additive in anhydrous cosmetics to provide oil control, help mitigate syneresis, and assist in high loading of oil into final products.
- Absorbent: Magnesium carbonate is often used to absorb perfume before incorporation into face powders. The porous structure of magnesium carbonate gives the material an enormous amount of surface area, which in turn allows it to absorb more oil and excess moisture compared to other commonly used ingredients. The material is semi-translucent on the skin, making it a suitable ingredient for makeup applications. It’s especially common in powders targeted toward oil control since its starch absorbs oil from the skin.
- Abrasive in Dentifrices: Magnesium Carbonate contributes to the physical cleaning effect and stain removal of toothpaste as well as increasing the gloss of the teeth. Abrasives in toothpaste are usually finely-ground particles that are able to clean the teeth and remove discoloration to a certain extent without damaging or wearing away the enamel.
- Mild Astringent: Basic magnesium carbonate is used as clay in face masks and it has mild astringent properties to smooth and soften skin. It is recommended for use on normal to dry skin.
Product Examples
Magnesium Carbonate has proven useful in a wide range of color cosmetic applications, including pressed, loose, and liquid formulations.
| Type | Examples |
| Primers | Face Primers, Primer Sticks, Pore Minimizing Mousse |
| Lip Color | Matte Lip Color |
| Powders | Setting Powders, Finishing Powders, Powder Blushes, Highlighters, Contour Powders |
| Foundation | Matte Foundation Sticks, Powder Foundation |
| Hair Care | Dry Shampoo |
Properties of Magnesium Carbonate
| Appearance at 25°C | White, yellowish, grayish-white, or brown powder crystalline powder; Hygroscopic |
| Molar Mass | 84.3139 g/mol (anhydrous) |
| Density at 25°C | 2.958 g/cm3 (anhydrous) |
| Solubility | Practically insoluble in water, acetone, ammonia. It dissolves in diluted acids with effervescence. |
| Bulk Density (untapped) | 0.42 g/cc |
| Relative Density (water = 1) | 2.95 |
| Tapped Density (1000 taps) | 0.55 g/cc |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Refractive Index | 1.717 (anhydrous) |
| Melting Point | 350°C (662 °F; 623 K) |
| Shelf Life | 24-36 months |
| Storage Condition | Store in its original package, tightly sealed in a dry, well-ventilated place. Exposure to moisture may cause caking. |
Typical Formulations
Magnesium Carbonate Formulation Phases
Cream to Powder Foundation
| PHASE | INCI NAME | % Wt. |
| A | Octyl Palmitate | 18.75 |
| Octyldodecanol | 15.75 | |
| Isopropyl Myristate | 12.60 | |
| Hydrogenated Coco-Glyceride | 10.50 | |
| Candelilla Wax | 10.50 | |
| Carnauba Wax | 1.00 | |
| Magnesium Carbonate | 1.00 | |
| Tocopheryl Acetate | 0.50 | |
| Dimethicone | 0.50 | |
| Propylparaben | 0.10 | |
| B | Aluminum Starch Octenylsuccinate and Lauroyl Lysine | 18.40 |
| Silica | 0.25 | |
| Methylparaben | 0.15 | |
| C | Geopearl C Crystal Soft Silver (Fluorphlogopite and Titanium Dioxide) | 8.00 |
| Geopearl C Crystal Silk Bronze (Fluorphlogopite and Titanium Dioxide and Iron Oxides) | 2.00 | |
| Total: | 100 | |
Formulation Procedure
- Combine ingredients from Phase A.
- Heat Phase A to 80°C.
- Add Phase B to phase A and mix until uniform at 80°C.
- Add Phase C until uniform at 80°C.
- Cool to 70°C and poor into pans.
- Cool to room temperature.
Magnesium Carbonate Formulation Considerations
Magnesium carbonate is often used to absorb fragrance prior to mixing. The fragrance should be first added to the magnesium carbonate part of the formulation so it’s absorbed uniformly, leaving no lumps. Then proceed further to the final addition to the overall formulation.
Magnesium Carbonate Safety & Regulatory Considerations
FDA Information: Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (oral capsules and tablets) and listed as a GRAS chemical.
EU Information: Accepted as a food additive in Europe.
UK Information: Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK.
Identification Numbers
| CAS Number | 546-93-0 |
| EC Number | 208-915-9 |
The maximum usage level of magnesium carbonate is as follows.
| Category | Usage Level |
| Loose Face powder (perfume absorbent) | 1-3% |
| Toothpaste | 30-40% |
| Talcum Powder | 10-15% |
| Aerosol Color hair sprays | >0.18% |
Fun Facts About Magnesium Carbonate
- Magnesium carbonate is often used in taxidermy for whitening skulls. It can be mixed with hydrogen peroxide to create a paste, which is then spread on the skull to give it a white finish.